Run commands in the container
When managing Docker containers, you may need to connect to a running container. It is very helpful if you want to see what is happening inside the container. You can use the docker exec command, SSH into a running Docker container, or get a shell to the container.
Concepts
Before running commands inside a container, let's list a few related concepts:
- Running commands in containers is similar to host machine.
- Commands in containers alter the container's filesystem.
- You can change the user account within containers.
- Filesystem changes in containers require permission considerations.
- Software installed in non-persistent directories will be lost after redeploy.
Method of access to containers
Two methods for you to access container:
Access by docker exec commands
The docker exec command runs a new command in a running container at your host machine.
# sample1
docker exec -it container_name bash
# sample2
docker exec -it container_name sh
# sample2
docker exec -it container_name ash
# sample4
docker run --name mycontainer -d -i -t alpine /bin/sh
You should know or try to get the shell environment of your container, it may bash, sh, or ash
Access container by Websoft9 Console
You can access container by Websoft9 Console which is the implementation of docker exec command.
-
Login to Websoft9 Console, go to application mangement from My Apps
-
Open the Containers tab, click
<>icon of Actions column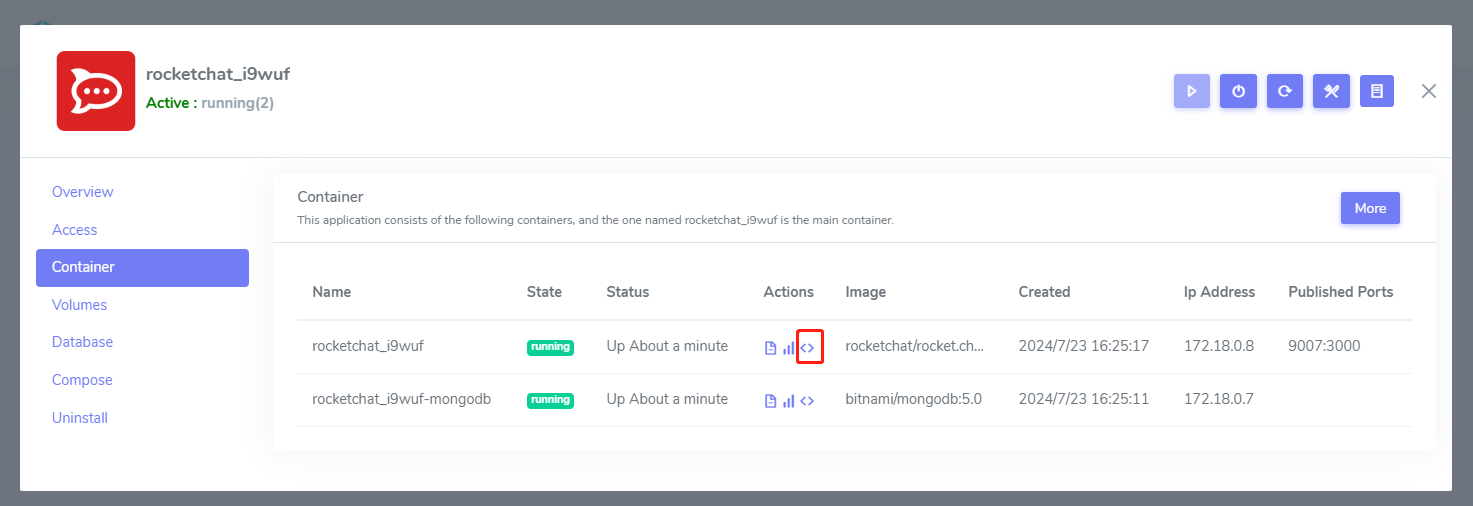
-
It will jump to the Container console and you can select the items and Connect container
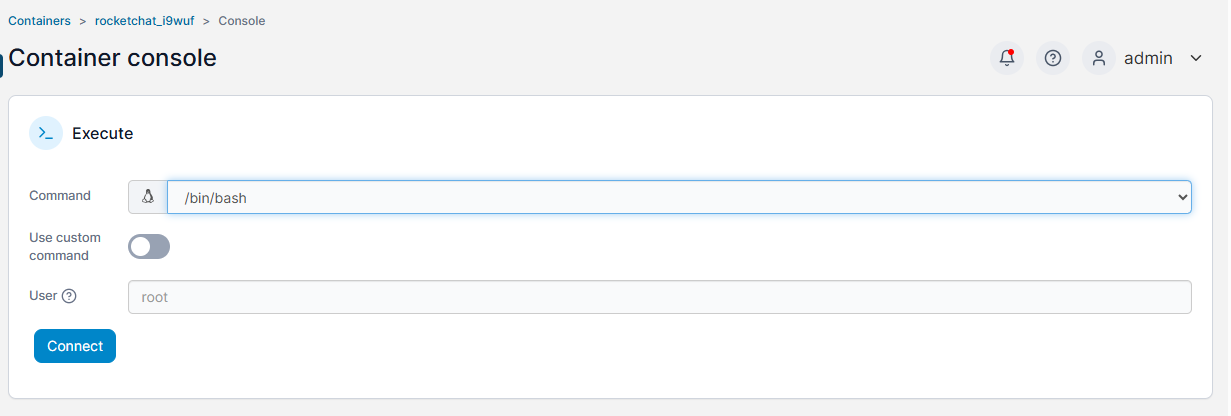
-
Once connection success, you can run shell command from terminal
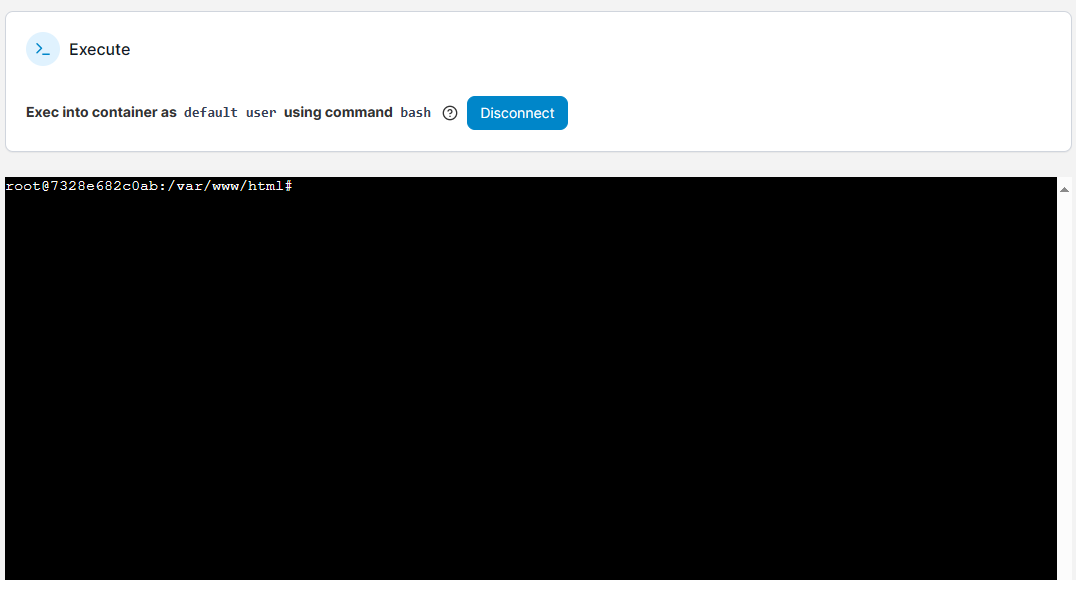
Commans samples
Install packages in the container
Install packages in the container is the same with host machine:
- Install by Linux repo tools:
apt,yum,dnf,pacman,zypper,apk - Download and compile
- Install by languages repo tools:
pip,npm,yarn,gem
Check system settings in the container
- Process and services:
top,ps aux - Get users:
cat /etc/passwd - Network:
netstat -tulnp,ss -tuln
Troubleshoot
Container permission issues?
- If the dockerfile does not create non-root user, the container will run as root by default.
- Container root equals host root, needs
--privileged=truefor same privileges. - You can switch users within the container using
su.