Gitlab Maintenance
This chapter is special guide for Gitlab maintenance and settings. And you can refer to Administrator and Steps after installing for some general settings that including: Configure Domain, HTTPS Setting, Migration, Web Server configuration, Docker Setting, Database connection, Backup & Restore...
Maintenance guide
Gitlab Backup and Restore
Based the official docs, we suggest you backup by these steps:
- Backup configuration files: Use SFTP compression and download(/etc/gitlab)
- Backup all GitLab system: run a backup command. (view the backup lists)
sudo gitlab-backup create - Put the system files and configuartion files in the same folder, named according to the date
- Backup completed
GitLab provide the official docs for Backups
Gitlab Upgrade
GitLab officially provides level by levelupgrade plan, each version has an upgrade The path must be gradually upgraded to the specified version, the method is as follows:
Specify version upgrade
The update method of updating to a specified version is very useful. On the one hand, it meets the requirements of a specific version of the user, and on the other hand, it achieves a gradual upgrade in this way, which solves the situation that the version span is too large to be upgraded.
For example: Gitlab12 to GitLab14 cannot be upgraded directly, you need to refer to the official step-by-step upgrade path to achieve this.
Take the Gitlab 13.0.14 to GitLab 14.1.6 as sample for your reference below:
-
Get the upgrade paths from official docs, computing your correct path like this:
13.0.14 -> 13.1.11 -> 13.8.8 -> 13.12.10 -> 13.12.12 -> 14.0.11 -> 14.1.6 -
Optional step: search all versions in GitLab repository (ce can be instead to ee)
# Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt-cache madison gitlab-ce
# RHEL/CentOS 6 and 7
yum --showduplicates list gitlab-ce
# RHEL/CentOS 8
dnf --showduplicates list gitlab-ce -
Update step by step
# Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt install gitlab-ce-<version>
# RHEL/CentOS 6 and 7
yum install gitlab-ce-<version>
# RHEL/CentOS 8
dnf install gitlab-ce-<version>
If you update by
yum install gitlab-cewhich not include version, it mean update to latest version
CE to EE
To upgrade an existing GitLab Community Edition (CE) server to GitLab Enterprise Edition (EE), all you have to do is install the EE package on top of CE.
- Get the CE version nubmer
# For Debian/Ubuntu
sudo apt-cache policy gitlab-ce | grep Installed
# For CentOS/RHEL
sudo rpm -q gitlab-ce - Match the EE version number.e.g. the CE number is 8.6.7-ce.0, then the EE number should be 8.6.7-ee.0
- Add the gitlab-ee Apt or Yum repository
# For Debian/Ubuntu
curl -s https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/gitlab/gitlab-ee/script.deb.sh | sudo bash
# For CentOS/RHEL
curl -s https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/gitlab/gitlab-ee/script.rpm.sh | sudo bash - Install the correct GitLab-EE version(system will automatically uninstall CE version the same time)
........................................
# For Debian/Ubuntu
........................................
## Make sure the repositories are up-to-date
sudo apt-get update
## Install the package using the version you wrote down from step 1
sudo apt-get install gitlab-ee=8.6.7-ee.0
## Reconfigure GitLab
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
........................................
# For CentOS/RHEL
........................................
## Install the package using the version you wrote down from step 1
sudo yum install gitlab-ee-8.6.7-ee.0.el7.x86_64
## Reconfigure GitLab
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure - Go to the GitLab admin panel of your server (/admin/license/new) and upload your license file.
- After you confirm that GitLab is working as expected, you may remove the old Community Edition repository:
# For Debian/Ubuntu
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/gitlab_gitlab-ce.list
# For CentOS/RHEL
sudo rm /etc/yum.repos.d/gitlab_gitlab-ce.repo
More details about CE upgrade to EE, please refer to official docs: Updating Community Edition to Enterprise Edition
Troubleshoot
In addition to the Gitlab issues listed below, you can refer to Troubleshoot + FAQ to get more.
Corporate fixed IP suddenly can't access Gitlab?
Phenomenon:Suddenly (previously accessible) Gitlab is not accessible through the corporate network (fixed IP), but can be accessed through your own mobile wifi.
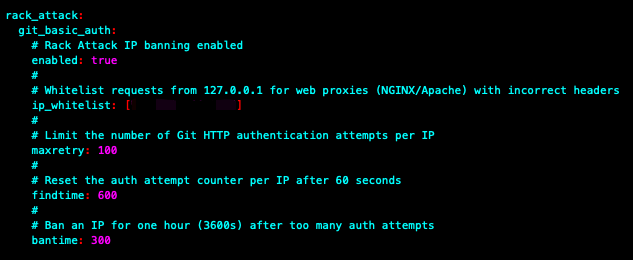
Why:GitLab has a rack-attack security mechanism. Under certain conditions (e.g., a large number of concurrent access to GitLab), rack-attack security will mistakenly block your IP, resulting in no access to GitLab from now on.
Solution:Modify the Gitlab Configuration file
GitLab 502 error when loading?
The minimum required free memory for GitLab is 4G. If the Server memory is limit, a 502 error will occur. For a single-core CPU server, the Unicorn and Sidekiq service starts up to a minute, and if it is not started, it will report a 502 error.
FAQ
Can I use GitLab Enterprise without a license?
If you have GitLab Enterprise installed, but did not import License, you are using all the features of Community Edition.。GitLab-EE vs GitLab-CE
GitLab support multi-language?
Yes, you can change the language from the Admin Panel of GitLab
Where is the database connection configuration of GitLab?
Database configuration information in /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb in the Gilab Configure
Can I remote connect PostgreSQL?
No, Omnibus GitLab use the PostgreSQL Peer Authentication mode for local connection
What is the default port for cloning gitlab Projects Using SSH?
Default port is 22
What is the password for the database root user?
Omnibus GitLab use the PostgreSQL Peer Authentication mode for local connection, no username and pssword
Is there a web-base GUI database management tools?
No
Is it possible to modify the repository path of GitLab?
Yes, Refer to official docs Repository Storage Paths