MySQL/MariaDB Study
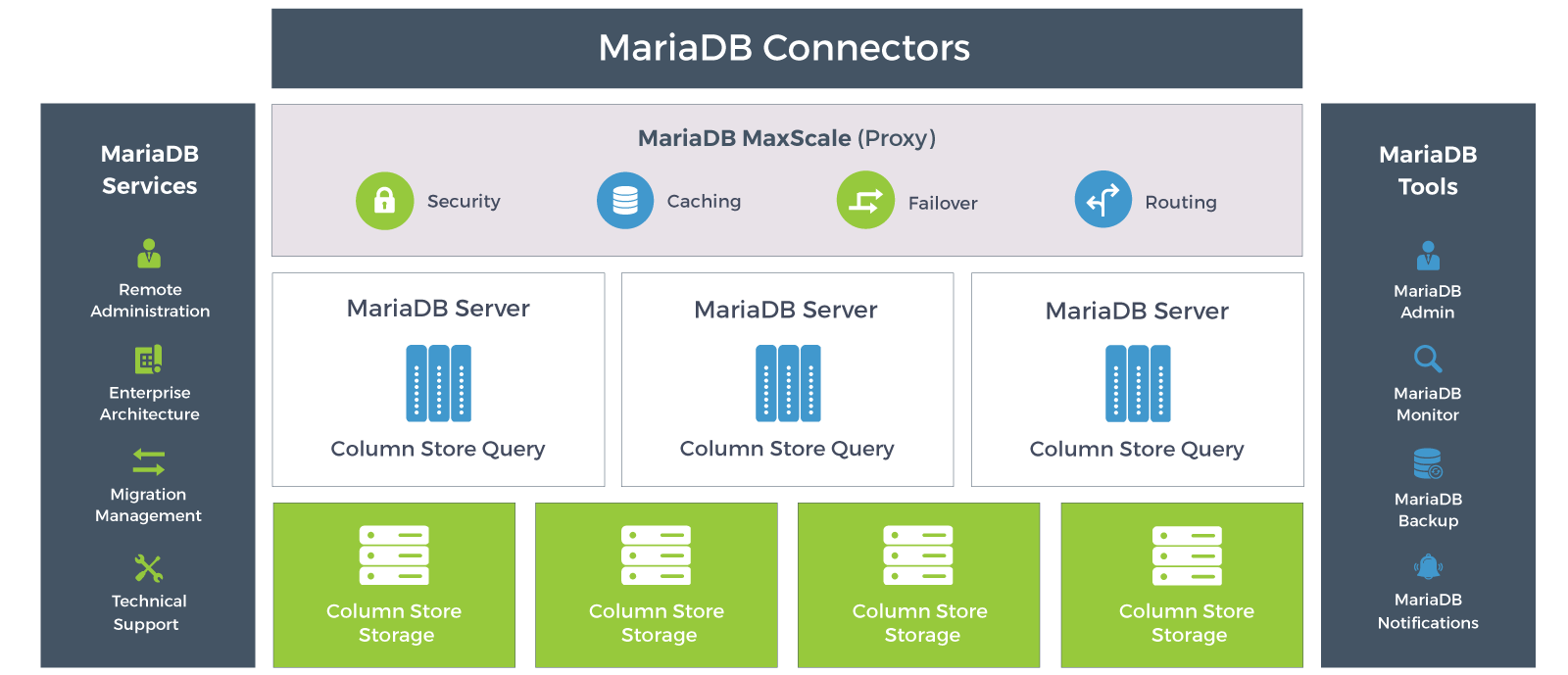
For MySQL/MariaDB administrators, the knowledge points to be mastered include:
- MySQL / MariaDB installation
- SQL statement
- Basic concepts: storage engine, character set
- Visual management: use visual tools such as phpMyAdmin to manage the database
- Advanced management technology: upgrade, use of client tools, log management, backup and recovery, monitoring
- Optimization technology: lock, connection pool, concurrent parameters, load balancing, cluster, master-slave, read-write separation
- Safety technology: injection
Next, we will make a brief exposition of the above points, hoping to help you in your study.
SQL
Language
SQL is an operation language (command) of the database. Once you log in to the database, you can use it to operate the database
- Under the command line, you can directly run SQL statements
- Under visualization, open the [run SQL] window to run SQL statements
There are three types of SQL:
- Database definition language (DDL): mainly used to create or modify database, data segment, table, column, index and other objects, mainly including create, drop, alter, etc
- Database manipulation language (DML): mainly used to add or update database records, including insert, delete, update, etc
- Database control statement (DCL): mainly used to control permissions and access, mainly including grant, revoke, etc
The following are some common SQL commands:
# Login database
mysql -u root –p
Enter password:
MariaDB> create database dbname; # create database
MariaDB> show databases; # view database
MariaDB> exit; # exit console
MariaDB> drop database databasename; # delete database
MariaDB> alter table tablename raname mytable # modify table name
In learning, we do not need to memorize every sentence, but we need to be able to locate "what sentence may be used in doing something" according to the official reference manual.
Pattern
SQL schema is the standard of SQL. Due to different manufacturers and different development stages, different SQL standards appear.
Popular SQL modes include ANSI, traditional and strict_ TRANS_ Tables, etc
Basic concepts
There is a big difference between the database system and the application software system. It is a system that stores, retrieves and calculates a large amount of standardized data.
Therefore, it needs users to understand some unique basic concepts:
Storage Engine
MariaDB storage engine refers to the type of database table. The storage engine determines the storage mode of the table in the computer.
Run show engines; , all supported storage engine types are listed:
MariaDB [(none)]> show engines;
+--------------------+---------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
| Engine | Support | Comment | Transactions | XA | Savepoints |
+--------------------+---------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
| CSV | YES | Stores tables as CSV files | NO | NO | NO |
| MRG_MyISAM | YES | Collection of identical MyISAM tables | NO | NO | NO |
| MEMORY | YES | Hash based, stored in memory, useful for temporary tables | NO | NO | NO |
| Aria | YES | Crash-safe tables with MyISAM heritage. Used for internal temporary tables and privilege tables | NO | NO | NO |
| MyISAM | YES | Non-transactional engine with good performance and small data footprint | NO | NO | NO |
| SEQUENCE | YES | Generated tables filled with sequential values | YES | NO | YES |
| InnoDB | DEFAULT | Supports transactions, row-level locking, foreign keys and encryption for tables | YES | YES | YES |
| PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA | YES | Performance Schema | NO | NO | NO |
+--------------------+---------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
8 rows in set (0.000 sec)
Only the InnoDB engine supports Transaction processing.
Character Set
MySQL's character set problem mainly includes two concepts, one is **character sets ** and the other is **collaborations **. The former is the character
content and coding, and the latter is the rules for proofreading the former. These two parameter sets can be specified at four levels: database instance, single database, table, column, and connection.
Run SHOW CHARACTER SET; , all supported character set types are listed:
MariaDB [(none)]> SHOW CHARACTER SET;
+----------+-----------------------------+---------------------+--------+
| Charset | Description | Default collation | Maxlen |
+----------+-----------------------------+---------------------+--------+
| big5 | Big5 Traditional Chinese | big5_chinese_ci | 2 |
| dec8 | DEC West European | dec8_swedish_ci | 1 |
| cp850 | DOS West European | cp850_general_ci | 1 |
| hp8 | HP West European | hp8_english_ci | 1 |
| koi8r | KOI8-R Relcom Russian | koi8r_general_ci | 1 |
| latin1 | cp1252 West European | latin1_swedish_ci | 1 |
| latin2 | ISO 8859-2 Central European | latin2_general_ci | 1 |
| swe7 | 7bit Swedish | swe7_swedish_ci | 1 |
| ascii | US ASCII | ascii_general_ci | 1 |
| ujis | EUC-JP Japanese | ujis_japanese_ci | 3 |
| sjis | Shift-JIS Japanese | sjis_japanese_ci | 2 |
| hebrew | ISO 8859-8 Hebrew | hebrew_general_ci | 1 |
| tis620 | TIS620 Thai | tis620_thai_ci | 1 |
| euckr | EUC-KR Korean | euckr_korean_ci | 2 |
| koi8u | KOI8-U Ukrainian | koi8u_general_ci | 1 |
| gb2312 | GB2312 Simplified Chinese | gb2312_chinese_ci | 2 |
| greek | ISO 8859-7 Greek | greek_general_ci | 1 |
| cp1250 | Windows Central European | cp1250_general_ci | 1 |
| gbk | GBK Simplified Chinese | gbk_chinese_ci | 2 |
| latin5 | ISO 8859-9 Turkish | latin5_turkish_ci | 1 |
| armscii8 | ARMSCII-8 Armenian | armscii8_general_ci | 1 |
| utf8 | UTF-8 Unicode | utf8_general_ci | 3 |
| ucs2 | UCS-2 Unicode | ucs2_general_ci | 2 |
| cp866 | DOS Russian | cp866_general_ci | 1 |
| keybcs2 | DOS Kamenicky Czech-Slovak | keybcs2_general_ci | 1 |
| macce | Mac Central European | macce_general_ci | 1 |
| macroman | Mac West European | macroman_general_ci | 1 |
| cp852 | DOS Central European | cp852_general_ci | 1 |
| latin7 | ISO 8859-13 Baltic | latin7_general_ci | 1 |
| utf8mb4 | UTF-8 Unicode | utf8mb4_general_ci | 4 |
| cp1251 | Windows Cyrillic | cp1251_general_ci | 1 |
| utf16 | UTF-16 Unicode | utf16_general_ci | 4 |
| utf16le | UTF-16LE Unicode | utf16le_general_ci | 4 |
| cp1256 | Windows Arabic | cp1256_general_ci | 1 |
| cp1257 | Windows Baltic | cp1257_general_ci | 1 |
| utf32 | UTF-32 Unicode | utf32_general_ci | 4 |
| binary | Binary pseudo charset | binary | 1 |
| geostd8 | GEOSTD8 Georgian | geostd8_general_ci | 1 |
| cp932 | SJIS for Windows Japanese | cp932_japanese_ci | 2 |
| eucjpms | UJIS for Windows Japanese | eucjpms_japanese_ci | 3 |
+----------+-----------------------------+---------------------+--------+
40 rows in set (0.000 sec)
The character set is actually a set of character symbols and codes. The corresponding characters and codes can convert the contents that can be recognized by human and the information that can be recognized by computer.
View
View is a new table derived from one or more tables, and this table is a virtual table.
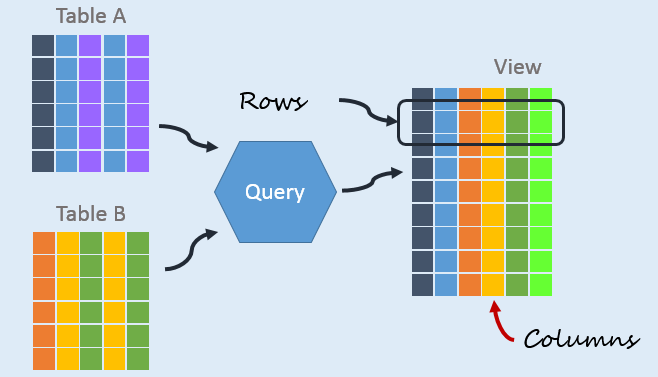
Views basically play a similar role to filtering and avoid duplicate table creation.
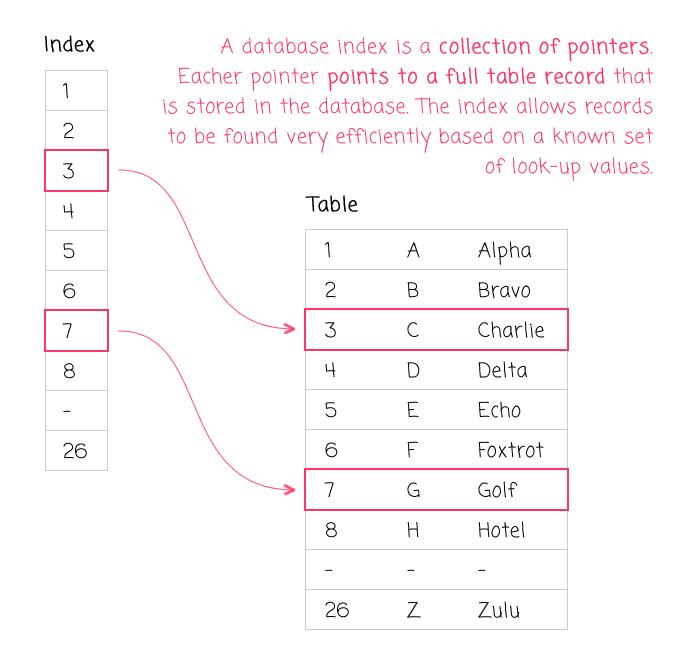
Index
Index as the name implies, it is a pointer table (called pointer in professional terms) established for the purpose of facilitating the rapid retrieval of data, similar to the phonetic order table in Xinhua dictionary.
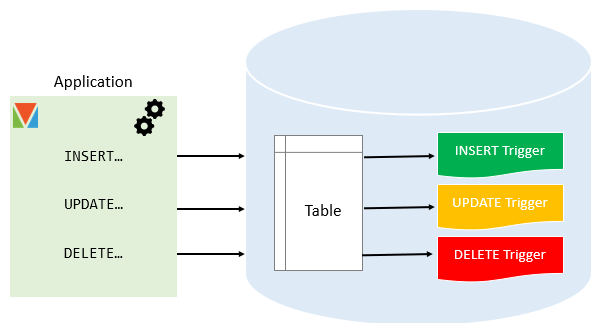
Triggers
Triggers are specific operations triggered by events such as insert, update and delete. When the trigger conditions of these triggers are met, the database system will execute the program statements defined by the triggers.
Transaction
Transaction is mainly used to process data with large amount of operation and high complexity. For example, in the personnel system, if you delete an employee, you need to delete both the basic information of the employee and the information related to the employee, such as salary slip and attendance data. In this way, these database operation statements constitute a transaction. The transaction starts with the begin statement and ends with the commit statement:
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into runoob_transaction_test value(5);
Query OK, 1 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into runoob_transaction_test value(6);
Query OK, 1 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> commit;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Generally speaking, a transaction must satisfy four conditions (acid): atomicity (or inseparability), consistency, isolation (also known as independence), and durability.
The popular explanation is as follows: "either succeed or recover after failure."
Stored procedure
A stored procedure is a program segment based on SQL that is written in advance in the database for the application to call.
Since it is a program segment, it certainly supports common program syntax: function, conditional judgment, loop, etc. Popular explanation: "database SQL programming"
Zoning
Partition is a physical database design technology, which mainly divides a logical single table into dozens of physical partitions. Its main purpose is to reduce the total amount of data read and write in a specific SQL operation to reduce the response time.
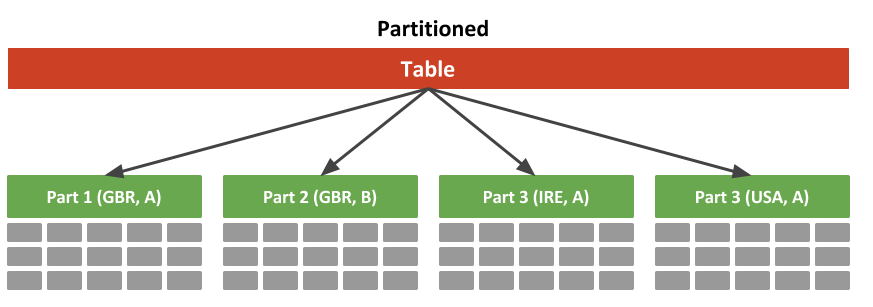
Senior management
User rights
MariaDB users mainly include root users and ordinary users. The root user is the administrator and has the most advanced database permissions.
Generally speaking, the user will not change the settings of the root user. Let's focus on ordinary users.
User management includes two knowledge points:
- User account information
- User account authority
In MariaDB, a user's account is composed of * * Username: host: password * *. MariaDB has a database named * * MySQL * * by default. It stores tables related to user accounts and user permissions. When users log in to the database, they can judge which permissions they have according to these tables, so as to realize permission control.
Tables related to user rights include (sorted by priority):
【user】>【db】>【host】>【table-priv】>【columns-priv】>【proc-priv】
From the dimension of permission size, they are: system, database, table, view, index, stored procedure, etc The following is the table structure information of the user table:
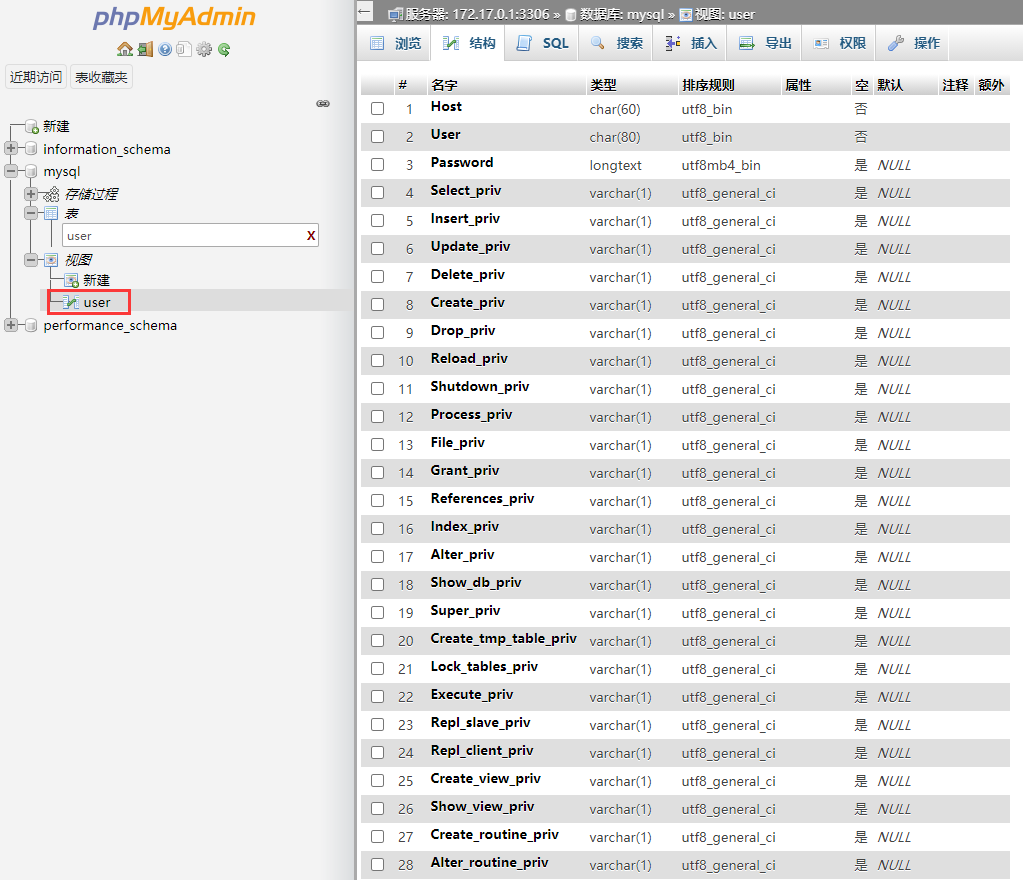
There is a special command * * grant * *, which is used to authorize other users (including themselves).
###Backup restore
First, define the terms related to backup:
In terms of the object data format of the backup, the backup is divided into:
- Logical backup: the backup realized by [exporting] the database
- Physical backup: the backup realized by copying the physical files of the database
From the database state during backup, backup can be divided into:
- Cold backup: backup after database shutdown
- Hot backup: database backup without shutdown (data integrity must be maintained)
MariaDB supports three backup and restore methods:
- Backup and recovery tools: mysqldump or mysqlhotcopy
- Copy data directory
- Export import table
mysqldump is an official command, simple and practical:
# Backup one, multiple and all databases respectively
mysqldump -u usename -p dbname > dbname.sql
mysqldump -u usename -p dbname1 dbname12 > dbname.sql
mysqldump -u usename -p --all-database > all-database.sql
Upgrade
Please refer to the update and upgrade chapter of this article for details.
Management tool
MariaDB after installation, the following tools are available by default:
- mysql
- mysqladmin
- mysqldump
- mysqlhotcopy
- mysqlcheck
- mysqlshow
- mysqlimport
- mysqlbinlog
- myisampack
Log
MariaDB log is a file that records daily operation and error information of MariaDB database. It can be divided into:
- Binary log (binlog)
- Error log
- Slow query log
- General query log
The binary log records all actions of operating the database and is applicable to restoring the database; The error log is suitable for diagnosing problems; Slow query log is used to record query statements with low execution efficiency; General query log records all query operations;
From the perspective of troubleshooting, error logs and slow query logs are the log objects that need to be considered.
###Monitoring
Database monitoring is mainly through monitoring tools to actively find abnormalities and promote subsequent fault operation and maintenance processes.
Open source software related to database monitoring includes:
- Nagios
- Cacti
- Zabbix
- Ganglia
Optimize
Optimization is to improve the performance of the database by analyzing the status of a certain time period of the database, adjusting parameters and improving computing resources.
Below we will focus on the introduction to Optimization:
- Login in MariaDB database
- Run
show status like 'vaule', view performance related parameters and diagnose overall performanceMariaDB [(none)]> show status like 'connections';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| Connections | 12 |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.000 sec)
- Connection: connection times
- Uptime: server online time
- slow_ Queries: slow query times
- com_ Select: query operation times
- com_ Insert: number of insert operations
- com_ Update: number of update operations
- com_ Delete: number of delete operations
-
Use index and view to reduce database retrieval
-
Split a large table (with many fields) into multiple small tables
-
Analyze and optimize table
analyze table name -
Optimize server configuration
-
Optimize my Cache and memory configuration items in CNF (* * master can control * *)
Security
The unique security risk of the database comes from the SQL injection problem.
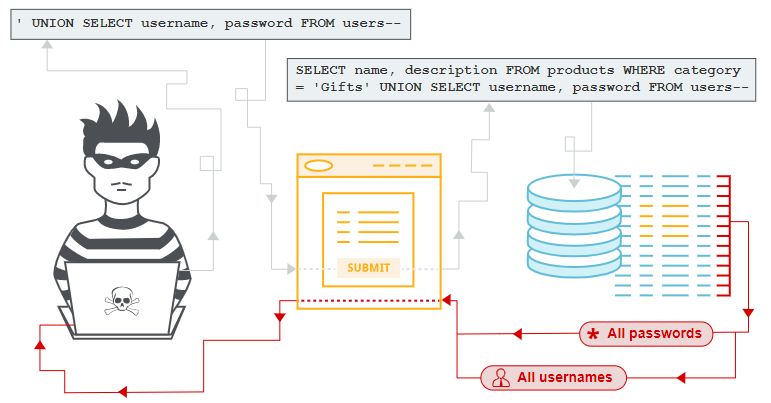
Audit
With the rapid development of the global digital economy, the accompanying data security has become a major hidden danger. At present, all countries have introduced laws related to network security, and made clear provisions on data protection and privacy management.
Database security is the top priority. Database audit is to track the utilization rate and authority of database resources, especially to monitor and record user database operations. The audit meets increasingly strict compliance requirements.
The audit can be based on a variety of factors, including a single operation (for example, the type of SQL statement executed) or a combination of factors (for example, user name, application, time, etc.). Performing regular database log analysis can enhance internal security measures by answering questions such as who changed critical data and when.

How to start the audit of MariaDB?
- Install Maria Audit Plugin plugin
- Set audit log path
Advanced architecture
High availability is mainly considered from the aspects of read-write separation, master-slave and cluster.
Read write separation
Master slave replication
MariaDB master-slave replication is to transfer the DDL and DML operations of the master database to the replication server (also called slave database) through binary logs, and then re execute these logs on the slave database (also called redo), so as to keep the data of the slave database and the master database synchronized.
MariaDB supports the replication of one master library to multiple slave libraries. The slave library can also be used as the master library of other servers to realize the chain architecture.
Master slave replication application scenario:
- If there is a problem with the master library, you can quickly switch to the slave library to provide services
- Query from the database to reduce the access pressure of the main database
- Perform backup from the library to avoid affecting the service of the primary library during backup
Because replication is asynchronous or semi synchronous, there is always a certain gap between master and slave data.