MongoDB Maintenance
This chapter is special guide for MongoDB maintenance and settings. And you can refer to Administrator and Steps after installing for some general settings that including: Configure Domain, HTTPS Setting, Migration, Web Server configuration, Docker Setting, Database connection, Backup & Restore...
Maintenance guide
MongoDB Backup
Run the following command to back up the data file in the following folder of mongodb application directory: data/mongo_data/dump/admin. The general manual backup operation steps are as follows:
- Access MongoDB container
docker exec -it mongodb cd /data/db - Use the tool mongodump to export database
#1 backup
mongodump --authenticationDatabase admin --username root --password PASSWORD -d DATABASE_NAME -h localhost
# check you backup
cd dump/admin && ls - Use tool mongorestore to restore database
mongorestore --authenticationDatabase admin --username root --password PASSWORD PATH_TO_BACKUP_FILE
More details please refer to official docs: MongoDB Backup Methods
MongoDB Upgrade
More detail refer to official docs:Upgrade to the Latest Revision of MongoDB
MongoDB Data Migration
Edit configuration file: /data/apps/mongodb/src/mongod.conf
Troubleshoot
In addition to the MongoDB issues listed below, you can refer to Troubleshoot + FAQ to get more.
MongoDB compass is unable to connect to the database?
Check whether the connection fields such as 27017 port, bindip and account authentication meet the conditions
FAQ
What are the Client and Server of MongoDB?
MongoDB Server refers to the MongoDB program ontology, and MongoDB Client refers to the client that uses TCP protocol to connect to the program local. They are two completely different programs, which means that they do not need to be installed on the same service at the same time.
What's difference between command mongod and mongo?
- mongod is the command for start MongoDB server's service
- mongo is MongoDB shell
MongoDB Community vs MongoDB Enterprise?
MongoDB Community is the source available and free to use edition of MongoDB.
MongoDB Enterprise is available as part of the MongoDB Enterprise Advanced subscription and includes comprehensive support for your MongoDB deployment. MongoDB Enterprise also adds enterprise-focused features such as LDAP and Kerberos support, on-disk encryption, and auditing.
Could I directly access mongodb without authentication?
Yes, MongoDB does not enable access control during installation by default. So it can be accessed without mongodb user name and password, e.g. through this URL:mongodb://localhost/admin.
MongoDB Enable Access Control
What is the admin database of MongoDB?
The MongoDB installation will include an admin database by default. If you create an administrator account, you must store it in this admin
Which authentication MongoDB support?
MongoDB provides various features, such as authentication, access control, encryption, to secure your MongoDB deployments. Some key security features include:
MongoDB also provides the Security Checklist for a list of recommended actions to protect a MongoDB deployment.
What platforms does MongoDB support?
For the list of supported platforms, see Supported Platforms.
What are the official tools of MongoDB?
The main official tools are as follows:
MongoDB Atlas Open Service Broker
Learn how you can use the Atlas Open Service Broker to deploy Atlas clusters and manage database users from within Kubernetes.
MongoDB BI Connector
Reference guide for the MongoDB BI Connector. Learn how you can use business intelligence tools and SQL to query data stored in MongoDB.
MongoDB Charts
Reference guide for MongoDB Charts. Learn how to create visualizations of MongoDB data quickly and easily.
MongoDB Command Line Interface
Learn how to use the MongoDB Command Line Interface to quickly interact with your MongoDB deployments for easier testing and scripting.
MongoDB Compass
Reference guide for MongoDB Compass. Learn to use MongoDB Compass's graphical user interface to view and analyze data stored in MongoDB.
MongoDB Database Tools
Tools for interfacing with a MongoDB cluster, such as importing/exporting data.
MongoDB Kafka Connector
Learn how to persist data from Kafka topics as a data sink into MongoDB as well as publish changes from MongoDB into Kafka topics as a data source.
MongoDB Kubernetes Operator
Learn how you can use the Kubernetes Operator to run MongoDB Enterprise on Kubernetes and configure Cloud or Ops Manager for backup and monitoring.
MongoDB Spark Connector
Reference guide for the MongoDB Spark Connector. Learn how you can use MongoDB with Apache Spark.
What other MongoDB client tools besides MongoDB Compass?
The GUI of MongoDB are divided into desktop version and web version. Each form of tool has some popular tools:
Desktop
- MongoDB Compass Community - A free tool for developing with MongoDB and includes a subset of the features of Compass.
- dbKoda - Cross-platform and open-source IDE
- MongoHub - Mac native client
- Mongotron - Cross-platform and open-source client built with Electron
- NoSQLBooster - Feature-rich but easy-to-use cross-platform IDE (formerly MongoBooster)
- Nosqlclient - Cross-platform, self hosted and easy to use management tool (formerly Mongoclient)
- Robo 3T - Free, native and cross-platform shell-centric GUI (formerly Robomongo)
- Studio 3T - Cross-platform GUI, stable and powerful (formerly MongoChef)
Web GUI
- adminMongo - Web-based user interface to handle connections and databases needs
- mongo-express - Web-based admin interface built with Express
- mongoadmin - Admin interface built with Django
- mongri - Web-based user interface written in JavaScript
- Rockmongo - PHPMyAdmin for MongoDB, sort of
What is NoSQL?
NoSQL is the abbreviation of not only SQL, not not not SQL, which means that NoSQL database also has the query concept similar to SQL.
NoSQL is an all encompassing term that covers all databases except the traditional relational database (RDBMS). NoSQL tries to give up
the traditional structure of relational database, so that developers can realize the model in a way closer to the system data flow requirements.
There are many different NoSQL technologies, including:
- Document storage database
- Key / value database
- Column storage database
- Figure storage database
Mongodb is an outstanding representative of document storage database. The document database uses the document oriented method to store data.
The idea behind it is that all data of a single entity can be stored in one document, and the documents are combined in the form of sets.
Mongodb uses bson (a lightweight binary JSON) format to store data. Each document can not exceed 16MB at most, so as to avoid too much memory or
frequent access to the file system. Therefore, the performance is very high.
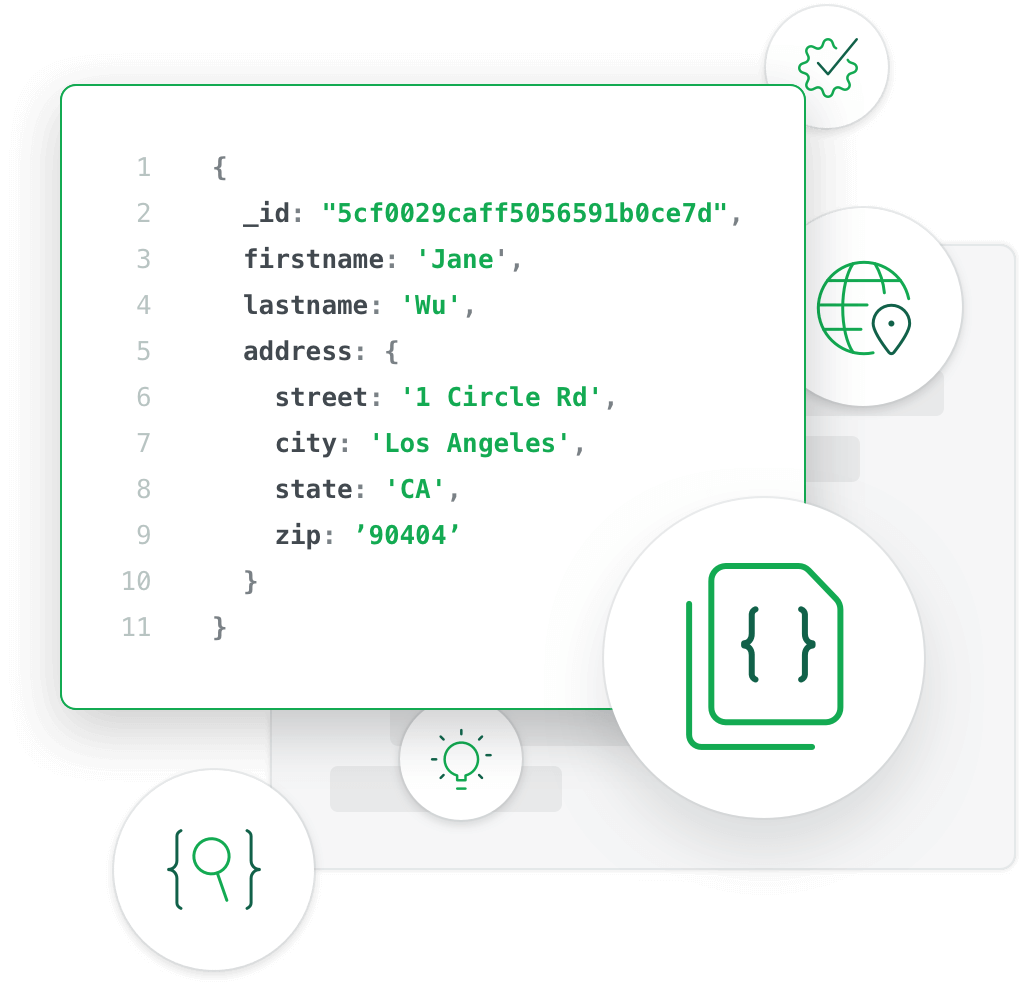
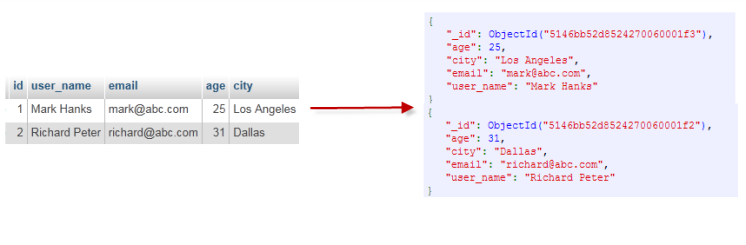
SQL vs MongoDB ?
The basic concepts in mongodb are document, collection, and databases. let's take SQL as an example to help you better understand MongoDB.
| SQL Term/concept | MongoDB Term/concept | explain |
|---|---|---|
| database | database | Database Instance |
| table | collection | databae table/collection |
| row | document | table row/document |
| column | field | Data field/domain |
| index | index | index |
| table joins | MongoDB no this | |
| primary key | primary key | keyPrimary key, MongoDB automatically sets the _id field as the primary key |
Through the example below, we can also understand some concepts in Mongo more intuitively:
What data types does MongoDBhave?
Mongodb's data type is very similar to JavaScript objects.
String - this is the most commonly used data type for storing data. The string in mongodb must be 'UTF-8'.
Integer - this type is used to store numeric values. The integer can be '32' bit or '64' bit, depending on the server.
Boolean type - this type is used to store Boolean values (true '/ false').
**Double precision floating-point number * * - this type is used to store floating-point values.
Min/Max key - this type is used to compare the value with the minimum and maximum ` bson 'elements.
Array - this type is used to store an array or list or multiple values in one key.
Timestamp - `ctimestamp'. When a document is modified or added, it can be recorded conveniently.
Object - this data type is used for embedded documents.
Object - this data type is used for embedded documents.
Null - this type is used to store 'null' values.
Symbol - the data type is the same as the string; However, the language used to use specific symbol types is usually reserved.
Date - this data type is used to store the current date or time in UNIX time format. You can specify the date and time you need by creating a date object and specifying the date of day, month and year.
Object ID - this data type is used to store the ID of the document.
Binary data - this data type is used to store binary data.
Code - this data type is used to store JavaScript code into the document.
**Regular expression * * - this data type is used to store regular expressions
Database, user and role relationship in mongodb?
Read the following code to understand the relationship between users, databases and roles:
use reporting
db.createUser(
{
user: "reportsUser",
pwd: "12345678",
roles: [
{ role: "read", db: "reporting" },
{ role: "read", db: "products" },
{ role: "read", db: "sales" },
{ role: "readWrite", db: "accounts" }
]
}
)
For mongodb, each user exists in a database (different from mysql, where all users are stored in a system database)
By default, the system will automatically create an admin database. This is a special database that provides functions that are not available in ordinary databases. Database users with global management permissions must be stored in this admin database.